What is the difference between a fire pump and fire hydrant?
A fire pump and a fire hydrant are both crucial components in a fire protection system, but they serve different functions and are used in different scenarios.
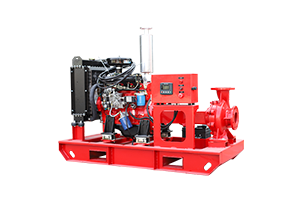
Fire Pump
A fire pump is a device that increases water pressure to ensure adequate flow to a fire protection system, such as sprinklers or standpipes, especially in buildings where the water supply pressure is insufficient on its own. Fire pumps are typically powered by electric motors or diesel engines and are activated when water pressure in the system drops below a certain level, usually during the activation of sprinklers or hoses.
- Purpose: Increases water pressure to meet the demand of the fire suppression system.
- Placement: Located in buildings with extensive fire protection needs or high-rises where water must be pumped to upper floors.
- Operation: Often part of a fire pump package and operates only when needed.
Fire Hydrant
A fire hydrant is an external connection point for firefighters to access water from the municipal water supply or other sources to combat fires. Hydrants are placed at various locations in public or private areas, allowing firefighters to connect hoses and draw water directly.
- Purpose: Provides a direct water source for firefighting crews.
- Placement: Found outdoors along streets or within industrial and commercial premises.
- Operation: Used manually by firefighters to connect hoses for fire suppression activities.
Key Differences
- Functionality: Fire pumps boost water pressure for internal building systems, while fire hydrants provide an outdoor water source for firefighting.
- Usage Scenario: Fire pumps are part of a building’s internal fire protection system, whereas hydrants are used by firefighters to access water on-site.
In essence, a fire pump ensures adequate water flow and pressure within a building, while a fire hydrant gives firefighters access to water for external firefighting needs.