What are the key differences between diesel and electric fire pumps?
Aug 30, 2024
Share:
The key differences between diesel and electric fire pumps primarily relate to their power sources, installation requirements, operational characteristics, and maintenance needs. Here’s a detailed comparison of the two types of fire pumps:
### 1. **Power Source**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:** Powered by a diesel engine. They operate independently of the electrical power supply, making them ideal for situations where electrical reliability is a concern, such as in areas prone to power outages.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:** Powered by an electric motor. They require a reliable electrical power supply and are often connected to the building’s main electrical system or a dedicated generator.
### 2. **Installation Requirements**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Fuel Storage:** Require a separate diesel fuel storage tank, fuel lines, and a fuel delivery system.
- **Ventilation and Exhaust:** Need proper ventilation to prevent the buildup of exhaust gases and adequate space for the exhaust system.
- **Physical Space:** Generally require more space for installation due to the size of the diesel engine, fuel tank, and associated components.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Electrical Infrastructure:** Require a robust electrical supply with dedicated circuits, switchgear, and possibly an emergency generator or backup power source.
- **Space Requirements:** Typically require less physical space compared to diesel pumps, as they don’t need a fuel tank or exhaust system.
### 3. **Operational Characteristics**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Independence from Electrical Supply:** Can operate independently of the electrical grid, which is beneficial during power failures or when electrical infrastructure is compromised.
- **Start-Up Time:** Generally have a slightly longer start-up time than electric pumps due to the engine needing to crank up.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Quick Start-Up:** Electric motors start almost instantly when activated, providing rapid response in emergencies.
- **Reliance on Power Supply:** Depend on a reliable power source; if power is lost and there is no backup generator, the pump will not function.
### 4. **Maintenance Requirements**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Regular Engine Maintenance:** Require more frequent and intensive maintenance, including oil changes, fuel filter replacements, battery checks, and periodic testing to ensure the engine starts and runs properly.
- **Fuel Management:** Diesel fuel needs to be managed carefully to avoid contamination, condensation, and degradation over time.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Less Maintenance:** Generally require less maintenance compared to diesel pumps, mainly focusing on electrical components, connections, and motor bearings.
- **No Fuel Management:** No need to handle fuel, making maintenance simpler and often less expensive.
### 5. **Cost Considerations**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Higher Initial Costs:** Typically have higher upfront costs due to the engine, fuel storage, and exhaust systems.
- **Higher Maintenance Costs:** More expensive to maintain due to the need for regular engine servicing and fuel management.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Lower Initial Costs:** Generally less expensive to install because they require fewer components (e.g., no need for fuel storage or exhaust systems).
- **Lower Maintenance Costs:** Typically have lower ongoing maintenance costs compared to diesel pumps.
### 6. **Environmental and Safety Considerations**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Emissions:** Produce exhaust emissions, which may require compliance with environmental regulations.
- **Fire Hazard:** Diesel fuel presents a fire hazard and requires careful handling and storage.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Cleaner Operation:** Do not produce exhaust emissions, making them more environmentally friendly.
- **Electrical Safety:** Electrical components must be properly insulated and grounded to prevent electrical hazards.
### Summary
Choosing between diesel and electric fire pumps depends on various factors, including the reliability of the local power supply, space availability, budget, and specific fire protection needs. Diesel fire pumps are favored in applications where electrical reliability is uncertain or where independence from the grid is crucial. Electric fire pumps are preferred in settings with reliable electricity, offering simplicity, lower maintenance, and quicker start-up times.
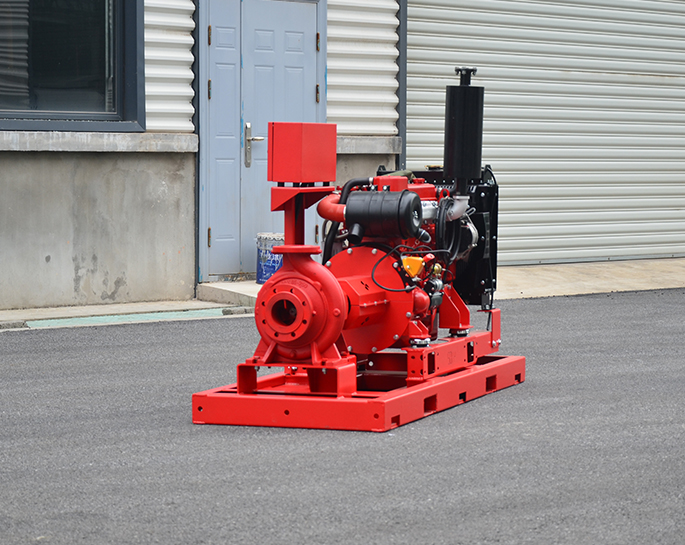
### 1. **Power Source**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:** Powered by a diesel engine. They operate independently of the electrical power supply, making them ideal for situations where electrical reliability is a concern, such as in areas prone to power outages.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:** Powered by an electric motor. They require a reliable electrical power supply and are often connected to the building’s main electrical system or a dedicated generator.
### 2. **Installation Requirements**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Fuel Storage:** Require a separate diesel fuel storage tank, fuel lines, and a fuel delivery system.
- **Ventilation and Exhaust:** Need proper ventilation to prevent the buildup of exhaust gases and adequate space for the exhaust system.
- **Physical Space:** Generally require more space for installation due to the size of the diesel engine, fuel tank, and associated components.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Electrical Infrastructure:** Require a robust electrical supply with dedicated circuits, switchgear, and possibly an emergency generator or backup power source.
- **Space Requirements:** Typically require less physical space compared to diesel pumps, as they don’t need a fuel tank or exhaust system.
### 3. **Operational Characteristics**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Independence from Electrical Supply:** Can operate independently of the electrical grid, which is beneficial during power failures or when electrical infrastructure is compromised.
- **Start-Up Time:** Generally have a slightly longer start-up time than electric pumps due to the engine needing to crank up.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Quick Start-Up:** Electric motors start almost instantly when activated, providing rapid response in emergencies.
- **Reliance on Power Supply:** Depend on a reliable power source; if power is lost and there is no backup generator, the pump will not function.
### 4. **Maintenance Requirements**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Regular Engine Maintenance:** Require more frequent and intensive maintenance, including oil changes, fuel filter replacements, battery checks, and periodic testing to ensure the engine starts and runs properly.
- **Fuel Management:** Diesel fuel needs to be managed carefully to avoid contamination, condensation, and degradation over time.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Less Maintenance:** Generally require less maintenance compared to diesel pumps, mainly focusing on electrical components, connections, and motor bearings.
- **No Fuel Management:** No need to handle fuel, making maintenance simpler and often less expensive.
### 5. **Cost Considerations**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Higher Initial Costs:** Typically have higher upfront costs due to the engine, fuel storage, and exhaust systems.
- **Higher Maintenance Costs:** More expensive to maintain due to the need for regular engine servicing and fuel management.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Lower Initial Costs:** Generally less expensive to install because they require fewer components (e.g., no need for fuel storage or exhaust systems).
- **Lower Maintenance Costs:** Typically have lower ongoing maintenance costs compared to diesel pumps.
### 6. **Environmental and Safety Considerations**
- **Diesel Fire Pumps:**
- **Emissions:** Produce exhaust emissions, which may require compliance with environmental regulations.
- **Fire Hazard:** Diesel fuel presents a fire hazard and requires careful handling and storage.
- **Electric Fire Pumps:**
- **Cleaner Operation:** Do not produce exhaust emissions, making them more environmentally friendly.
- **Electrical Safety:** Electrical components must be properly insulated and grounded to prevent electrical hazards.
### Summary
Choosing between diesel and electric fire pumps depends on various factors, including the reliability of the local power supply, space availability, budget, and specific fire protection needs. Diesel fire pumps are favored in applications where electrical reliability is uncertain or where independence from the grid is crucial. Electric fire pumps are preferred in settings with reliable electricity, offering simplicity, lower maintenance, and quicker start-up times.


.png)
.png)

.png)


