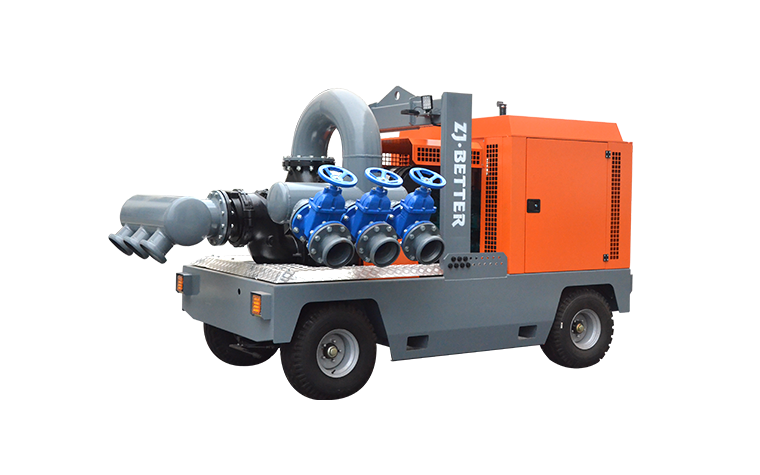
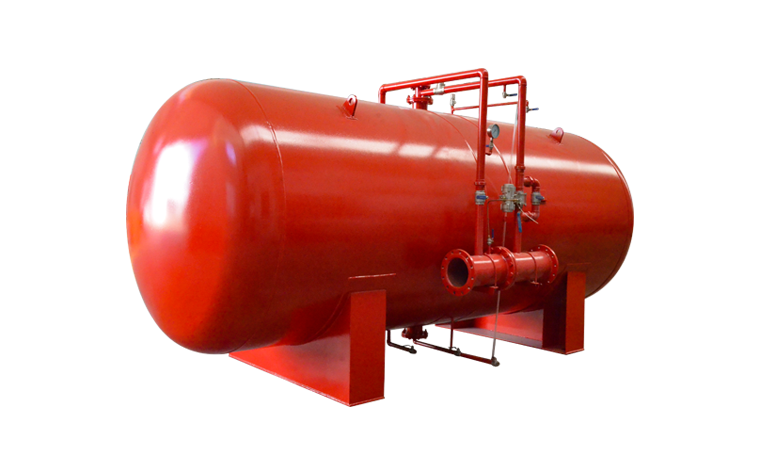
What are the key considerations for fire pumps in petrochemical plants and refineries?
Sep 04, 2024
Share:
When selecting and installing fire pumps in petrochemical plants and refineries, several key considerations are critical to ensure the safety, reliability, and compliance of the fire protection system:
### 1. **Compliance with Standards and Regulations**
- **NFPA 20**: The fire pump system must comply with the NFPA 20 standard, which governs the installation of stationary fire pumps.
- **Local Regulations**: Adhere to local fire codes, regulations, and insurance requirements specific to the region and industry.
- **Hazard Classification**: Ensure the fire pump system is designed to meet the hazard classification of the facility, which may be classified as high-risk due to the presence of flammable liquids and gases.
### 2. **Pump Selection**
- **Type of Pump**: Choose between electric, diesel, or steam-driven fire pumps based on the facility's power reliability and backup power considerations.
- **Flow and Pressure Requirements**: The pump must meet the required flow (gallons per minute or liters per second) and pressure (psi or bar) necessary for the fire suppression systems, including hydrants, sprinklers, and deluge systems.
- **Pump Material**: Use materials resistant to the specific chemicals present in the plant, as some chemicals may be corrosive.
### 3. **Redundancy and Reliability**
- **Backup Pumps**: Include redundant fire pumps (e.g., one electric and one diesel) to ensure continuous operation during a fire emergency, even if one pump fails or loses power.
- **Jockey Pumps**: Install jockey pumps to maintain system pressure and prevent the main fire pumps from cycling unnecessarily.
- **System Testing**: Regularly test the fire pumps as per NFPA 25 standards to ensure they function correctly during emergencies.
### 4. **Explosion-Proof Equipment**
- **Hazardous Area Classification**: Fire pumps and associated electrical equipment (e.g., control panels, motors) should be explosion-proof and suitable for installation in hazardous (classified) locations within the plant.
- **Ingress Protection (IP) Rating**: Ensure electrical components have a high IP rating to protect against dust, moisture, and chemicals.
### 5. **Water Supply**
- **Adequate Water Supply**: The fire pump must have access to a reliable and adequate water source, which could be from a dedicated fire water tank, reservoir, or municipal water supply.
- **Water Quality**: The quality of water (e.g., saltwater, freshwater) can affect the longevity and performance of the fire pump. Corrosion-resistant materials may be required if the water is corrosive.
### 6. **System Integration**
- **Integration with Fire Detection**: The fire pump system should be integrated with the facility’s fire detection and alarm systems to ensure automatic activation during a fire.
- **Monitoring and Control**: The fire pump should be monitored for operational status, and alarms should be in place to alert operators of any issues (e.g., low pressure, pump failure).
### 7. **Environmental and Operational Conditions**
- **Ambient Temperature**: Consider the ambient temperature of the installation area, as extreme temperatures can affect pump performance.
- **Vibration and Noise**: The installation area should be designed to minimize vibration and noise, which can affect both the pump's operation and the working environment.
### 8. **Maintenance and Accessibility**
- **Maintenance Access**: Ensure that the fire pump and its components are easily accessible for maintenance and inspection.
- **Spare Parts Availability**: Stock critical spare parts on-site to minimize downtime in the event of a failure.
### 9. **Cost Considerations**
- **Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Reliability**: Balance the initial installation costs with the long-term reliability and maintenance costs. Higher-quality materials and components may have a higher upfront cost but offer better performance and longevity.
- **Energy Efficiency**: Consider the energy efficiency of the fire pump, especially in continuous operations, to reduce operational costs.
### 10. **Training and Preparedness**
- **Operator Training**: Personnel should be trained in the operation and emergency procedures related to the fire pump system.
- **Emergency Response Plan**: The fire pump system should be part of the overall emergency response plan, with drills conducted regularly.
By addressing these considerations, petrochemical plants and refineries can enhance their fire protection systems, ensuring safety and compliance in high-risk environments.
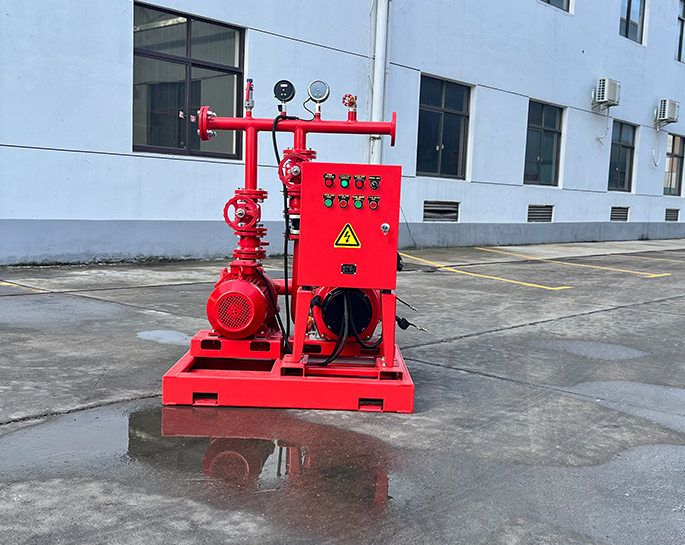

### 1. **Compliance with Standards and Regulations**
- **NFPA 20**: The fire pump system must comply with the NFPA 20 standard, which governs the installation of stationary fire pumps.
- **Local Regulations**: Adhere to local fire codes, regulations, and insurance requirements specific to the region and industry.
- **Hazard Classification**: Ensure the fire pump system is designed to meet the hazard classification of the facility, which may be classified as high-risk due to the presence of flammable liquids and gases.
### 2. **Pump Selection**
- **Type of Pump**: Choose between electric, diesel, or steam-driven fire pumps based on the facility's power reliability and backup power considerations.
- **Flow and Pressure Requirements**: The pump must meet the required flow (gallons per minute or liters per second) and pressure (psi or bar) necessary for the fire suppression systems, including hydrants, sprinklers, and deluge systems.
- **Pump Material**: Use materials resistant to the specific chemicals present in the plant, as some chemicals may be corrosive.
### 3. **Redundancy and Reliability**
- **Backup Pumps**: Include redundant fire pumps (e.g., one electric and one diesel) to ensure continuous operation during a fire emergency, even if one pump fails or loses power.
- **Jockey Pumps**: Install jockey pumps to maintain system pressure and prevent the main fire pumps from cycling unnecessarily.
- **System Testing**: Regularly test the fire pumps as per NFPA 25 standards to ensure they function correctly during emergencies.
### 4. **Explosion-Proof Equipment**
- **Hazardous Area Classification**: Fire pumps and associated electrical equipment (e.g., control panels, motors) should be explosion-proof and suitable for installation in hazardous (classified) locations within the plant.
- **Ingress Protection (IP) Rating**: Ensure electrical components have a high IP rating to protect against dust, moisture, and chemicals.
### 5. **Water Supply**
- **Adequate Water Supply**: The fire pump must have access to a reliable and adequate water source, which could be from a dedicated fire water tank, reservoir, or municipal water supply.
- **Water Quality**: The quality of water (e.g., saltwater, freshwater) can affect the longevity and performance of the fire pump. Corrosion-resistant materials may be required if the water is corrosive.
### 6. **System Integration**
- **Integration with Fire Detection**: The fire pump system should be integrated with the facility’s fire detection and alarm systems to ensure automatic activation during a fire.
- **Monitoring and Control**: The fire pump should be monitored for operational status, and alarms should be in place to alert operators of any issues (e.g., low pressure, pump failure).
### 7. **Environmental and Operational Conditions**
- **Ambient Temperature**: Consider the ambient temperature of the installation area, as extreme temperatures can affect pump performance.
- **Vibration and Noise**: The installation area should be designed to minimize vibration and noise, which can affect both the pump's operation and the working environment.
### 8. **Maintenance and Accessibility**
- **Maintenance Access**: Ensure that the fire pump and its components are easily accessible for maintenance and inspection.
- **Spare Parts Availability**: Stock critical spare parts on-site to minimize downtime in the event of a failure.
### 9. **Cost Considerations**
- **Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Reliability**: Balance the initial installation costs with the long-term reliability and maintenance costs. Higher-quality materials and components may have a higher upfront cost but offer better performance and longevity.
- **Energy Efficiency**: Consider the energy efficiency of the fire pump, especially in continuous operations, to reduce operational costs.
### 10. **Training and Preparedness**
- **Operator Training**: Personnel should be trained in the operation and emergency procedures related to the fire pump system.
- **Emergency Response Plan**: The fire pump system should be part of the overall emergency response plan, with drills conducted regularly.
By addressing these considerations, petrochemical plants and refineries can enhance their fire protection systems, ensuring safety and compliance in high-risk environments.