-
 Jul 27, 2023Vertical fire pump, how to choose single-stage or multi-stage?Choosing between a single-stage or multi-stage vertical fire pump depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of the fire protection system and the characteristics of the application. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Jul 27, 2023Vertical fire pump, how to choose single-stage or multi-stage?Choosing between a single-stage or multi-stage vertical fire pump depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of the fire protection system and the characteristics of the application. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Pressure Requirements: Determine the required discharge pressure for your fire protection system. Single-stage pumps are generally suitable for lower to moderate pressure requirements, while multi-stage pumps are more suitable for higher pressure demands. If your system needs high discharge pressure, a multi-stage pump might be the better choice.
Flow Rate: Consider the required flow rate (gallons per minute or liters per second) for your fire protection system. Single-stage pumps are typically used for lower flow rates, while multi-stage pumps can handle higher flow rates more efficiently.
Space Constraints: Evaluate the available installation space for the pump. Multi-stage pumps are usually more compact than single-stage pumps, which can be advantageous when space is limited.
Efficiency: Multi-stage pumps are generally more efficient than single-stage pumps at high-pressure applications. They are designed to handle higher heads with less power consumption, making them cost-effective in the long run.
NPSH Requirement: Consider the Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) available in your system. Multi-stage pumps typically require higher NPSH values compared to single-stage pumps. Ensure that the available NPSH meets the requirements of the chosen pump.
Maintenance: Evaluate the maintenance requirements of both types of pumps. Single-stage pumps often have fewer parts and may require less maintenance compared to multi-stage pumps, which have more components.
System Redundancy: Consider the redundancy requirements of your fire protection system. If redundancy is necessary for critical applications, you might need to install multiple single-stage pumps instead of one multi-stage pump.
Initial Cost: Generally, single-stage pumps are more cost-effective in terms of the initial purchase cost. Multi-stage pumps are typically more expensive due to their complex design.
Long-Term Cost: While single-stage pumps may have lower initial costs, multi-stage pumps might be more cost-effective in the long run due to their higher efficiency and potential energy savings.
Manufacturer and Model: Consult with reputable pump manufacturers and suppliers who can provide expert advice based on your specific requirements.
Ultimately, the choice between a single-stage and multi-stage vertical fire pump will depend on the unique needs and constraints of your fire protection system. Ensure that the selected pump meets the required pressure, flow rate, and efficiency for the intended application. Seek professional guidance if you are unsure about which type of pump is best suited for your specific scenario.
View details -
 Jul 27, 2023What are the characteristics of fire gas top pressure water supply equipment?"Fire gas top pressure water supply equipment" is not a commonly known term in the fire protection industry, and it is possible that the term used might be a local or specific term. However, based on the context, it seems like you might be referring to a high-pressure water supply system for firefighting purposes. In firefighting, water supply systems are essential to deliver sufficient water at high pressure to extinguish fires effectively.
Jul 27, 2023What are the characteristics of fire gas top pressure water supply equipment?"Fire gas top pressure water supply equipment" is not a commonly known term in the fire protection industry, and it is possible that the term used might be a local or specific term. However, based on the context, it seems like you might be referring to a high-pressure water supply system for firefighting purposes. In firefighting, water supply systems are essential to deliver sufficient water at high pressure to extinguish fires effectively.
If you are referring to a high-pressure water supply system, some general characteristics might include:
High Pressure Capability: The equipment is designed to provide water at high pressure to deliver strong and effective firefighting streams.
Pump System: It typically consists of a high-pressure pump capable of generating the required water pressure. These pumps could be electric, diesel-driven, or powered by other means.
Storage Tank: The system may include a water storage tank to ensure a continuous supply of water during firefighting operations.
Pressure Regulation: There may be pressure regulation devices or controls to maintain a consistent and suitable pressure for firefighting applications.
Rapid Deployment: The equipment is designed for quick deployment to provide an immediate water supply during emergencies.
Reliability: The system should be robust and reliable, ensuring it operates effectively during critical situations.
Compatibility: It should be compatible with various firefighting equipment, such as hoses, nozzles, and monitors.
Safety Features: Safety features, such as pressure relief valves and gauges, are essential to protect the system and the users.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to ensure the equipment remains in optimal condition for emergency use.
Compliance: The equipment should comply with relevant fire safety standards and regulations.
It's important to note that specific fire protection equipment and terminologies might vary by region or country due to different fire safety standards and practices. Therefore, if you are looking for equipment with this specific name or characteristics, it's recommended to consult local fire protection experts or suppliers for more accurate and relevant information.
View details -
 Jul 27, 2023How to solve the problem that the self-priming time of the self-priming pump is too long?If the self-priming time of a self-priming pump is too long, it indicates that the pump is having difficulty evacuating air from the suction line and priming itself. Several factors could contribute to this issue. Here are some steps to help you troubleshoot and solve the problem:
Jul 27, 2023How to solve the problem that the self-priming time of the self-priming pump is too long?If the self-priming time of a self-priming pump is too long, it indicates that the pump is having difficulty evacuating air from the suction line and priming itself. Several factors could contribute to this issue. Here are some steps to help you troubleshoot and solve the problem:
Check the Suction Line: Ensure that the suction line is free from any obstructions, debris, or clogs. A blocked or partially blocked suction line can impede the flow of water and lengthen the self-priming time.
Verify Check Valve Functionality: The check valve prevents water from flowing back into the suction line after priming. Check if the check valve is working correctly and replace it if it's malfunctioning or stuck.
Inspect the Foot Valve: The foot valve at the end of the suction line helps maintain the prime by holding water in the line. If the foot valve is faulty or damaged, it may not be sealing properly, leading to air entering the system. Inspect and clean the foot valve, and if necessary, replace it.
Check Impeller and Wear Plate: A worn or damaged impeller or wear plate can reduce the pump's self-priming efficiency. Inspect these components regularly and replace them if they show signs of wear.
Air Leaks: Check for air leaks along the suction line, pump housing, and fittings. Air leaks can disrupt the self-priming process and increase the priming time. Use a water and soap solution to identify and seal any air leak points.
Suction Lift Height: Verify that the pump is not operating beyond its designed suction lift height. Self-priming pumps have limitations on how high they can lift water. Operating beyond this limit can result in longer priming times.
Proper Water Level: Make sure the water source is deep enough to provide a sufficient water level for the pump to prime effectively. If the water level is too low, it will take longer for the pump to draw water into the system.
Venting the System: If the pump has a vent plug or priming port, ensure it is opened during the priming process. This helps release trapped air and aids in priming.
Pump Speed: Check if the pump is running at the correct speed. Running the pump too slowly can affect its ability to prime efficiently.
Maintenance: Regularly maintain the self-priming pump as per the manufacturer's guidelines. This includes cleaning, lubrication, and periodic replacement of worn parts.
Avoid Dry Running: Prevent the pump from running dry, as it can damage the impeller and wear plate, leading to reduced self-priming efficiency.
If the issue persists after checking and addressing these points, it may be necessary to consult the manufacturer's technical support or seek assistance from a qualified pump technician to diagnose and resolve the specific problem with your self-priming pump.
View details -
 Jul 27, 2023Daily cleaning of fire pumpsDaily cleaning of fire pumps is essential to ensure their proper functioning and readiness for emergency situations. Here are some steps to follow for daily cleaning:
Jul 27, 2023Daily cleaning of fire pumpsDaily cleaning of fire pumps is essential to ensure their proper functioning and readiness for emergency situations. Here are some steps to follow for daily cleaning:
Safety First: Before starting any cleaning or maintenance activity, ensure that the fire pump is shut down and disconnected from the power source to avoid any accidents.
Inspect the Surroundings: Check the area around the fire pump for any debris, dirt, or obstructions. Keeping the surroundings clean will prevent any foreign objects from entering the pump system.
Dust Removal: Use a soft brush or compressed air to remove dust and dirt from the external surfaces of the fire pump. Pay attention to vents and openings where debris may accumulate.
Check for Leaks: Look for any signs of leaks around the pump, hoses, and connections. Address any leaks promptly to prevent further damage and ensure the pump operates efficiently.
Inspect Intake Strainer: If the fire pump has an intake strainer, check and clean it daily. The strainer prevents debris from entering the pump's impeller and should be free from any blockages.
Check Fuel Level: Ensure that the diesel fuel tank has an adequate level of fuel for immediate use. Also, inspect for any fuel leaks or spillages.
Verify Battery Charge: If the fire pump uses a battery, check its charge level to ensure it is ready for operation.
Test Engine Starting: On a regular basis, engage the fire pump's engine to confirm it starts and runs smoothly.
Functional Test: If permitted by local regulations and safety protocols, conduct a brief functional test of the fire pump. Ensure that the pump achieves the required pressure and flow rate.
Monitor Gauges and Controls: Check all gauges and controls to verify they are functioning correctly and show appropriate readings.
Document Maintenance Activities: Keep a log of the daily cleaning and maintenance tasks performed, including any issues identified and actions taken.
Address Issues: If any problems or abnormalities are observed during the cleaning process, report them to the designated maintenance personnel for immediate investigation and resolution.
Remember that the daily cleaning is only one aspect of fire pump maintenance. Regular professional inspections and maintenance as per the manufacturer's guidelines should also be carried out to ensure the fire pump remains in optimal condition and ready for emergencies. Fire pump systems are critical safety equipment, and their proper upkeep is crucial for protecting lives and property.
View details -
 Jul 27, 2023Diesel engine fire pump maintenance knowledgeMaintaining a diesel engine fire pump is crucial to ensure its reliable operation in case of emergencies. Below are some essential maintenance tips for a diesel engine fire pump:
Jul 27, 2023Diesel engine fire pump maintenance knowledgeMaintaining a diesel engine fire pump is crucial to ensure its reliable operation in case of emergencies. Below are some essential maintenance tips for a diesel engine fire pump:
Regular Inspections: Schedule periodic inspections by a certified technician to assess the condition of the fire pump. Inspect the engine, fuel system, cooling system, electrical connections, and other critical components.
Fuel Quality: Ensure that the diesel fuel used is of high quality and meets the manufacturer's specifications. Contaminated or poor-quality fuel can lead to engine problems and reduce pump performance.
Fuel System Maintenance: Regularly clean and replace fuel filters to prevent debris from entering the engine. Water and sediment buildup in the fuel tank should also be drained periodically.
Lubrication: Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for lubrication. Check oil levels and change the engine oil at recommended intervals to ensure proper lubrication of engine components.
Cooling System: The cooling system is crucial for preventing engine overheating. Inspect coolant levels, check for leaks, and replace coolant as required.
Battery and Electrical System: Inspect and maintain the battery and electrical connections to ensure reliable engine starting. Clean any corrosion from terminals and replace weak batteries promptly.
Belt and Hose Inspection: Regularly inspect belts and hoses for signs of wear, cracking, or damage. Replace any worn or damaged components promptly.
Run Regular Tests: Perform routine tests of the diesel engine fire pump to verify its functionality. Regular testing will help identify potential issues and ensure the pump is ready for operation during emergencies.
Keep Surroundings Clean: Maintain a clean and debris-free environment around the fire pump to prevent clogging and reduce the risk of fire.
Follow Manufacturer's Guidelines: Always adhere to the maintenance guidelines provided by the fire pump manufacturer. These guidelines are tailored to the specific model and will help extend the life of the equipment.
Train Personnel: Ensure that the personnel responsible for maintaining and operating the diesel engine fire pump are well-trained and knowledgeable about its components and maintenance requirements.
Emergency Plan: Have a contingency plan in place in case the fire pump fails during an emergency. This plan should include alternative water sources or backup fire suppression systems.
Remember, regular maintenance is essential to keep the diesel engine fire pump in optimal working condition and ready to protect lives and property during critical situations. Always prioritize safety and follow best practices when handling and maintaining fire protection equipment.
View details -
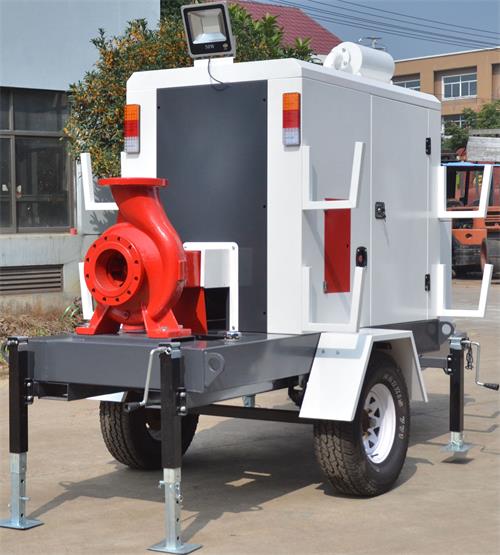 Jul 24, 2023How mobile fire pump work?When the rescue mission arrives, a flexible and reliable mobile pump truck can achieve drainage and drainage within 15 seconds to one minute after arriving at tView details
Jul 24, 2023How mobile fire pump work?When the rescue mission arrives, a flexible and reliable mobile pump truck can achieve drainage and drainage within 15 seconds to one minute after arriving at tView details