How to Conduct a Fire Pump Flow Test for Compliance
Fire pumps are crucial components in maintaining fire safety standards in commercial, industrial, and residential buildings. Regular fire pump flow testing ensures your system is compliant with fire safety regulations and operational during an emergency. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the necessary steps to conduct a fire pump flow test and ensure compliance with the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards.
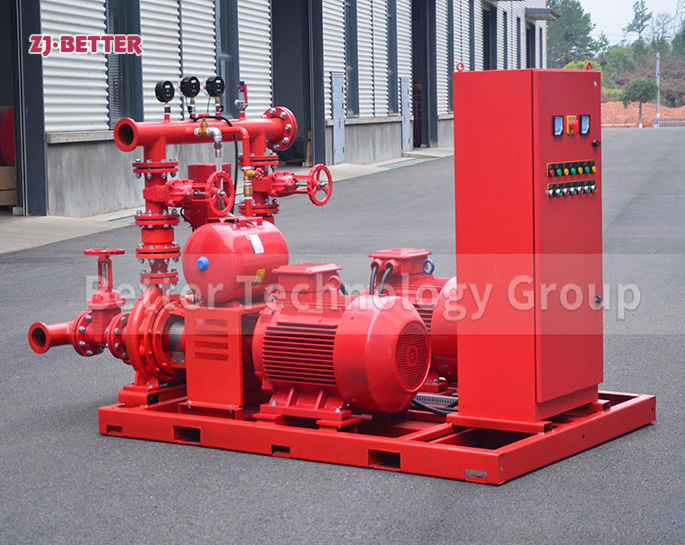

1. Understand the Compliance Standards
Fire pump testing is regulated by NFPA 25, the standard for the inspection, testing, and maintenance of water-based fire protection systems. According to NFPA 25, fire pumps must be tested annually to verify that they can deliver the required water flow and pressure for fire suppression.
2. Prepare the Testing Equipment
Before starting the test, gather the necessary tools:
- Flow test gauge: For measuring water flow and pressure.
- Pressure gauge: For recording pump pressure.
- Pitot tube: For measuring nozzle pressure.
- Data recorder: To track readings during the test.
Ensure the equipment is calibrated and in good working condition to produce accurate results.
3. Test the Fire Pump’s Flow Capacity
The primary goal of the fire pump flow test is to measure the pump’s ability to deliver the required flow and pressure at specific points. Here’s how to perform the test:
- Start the pump: Ensure that the fire pump starts automatically when the system detects a drop in pressure.
- Measure flow: Using the flow test gauge, measure the amount of water being pumped per minute (GPM). Refer to the pump's design specifications to confirm that it meets the required flow rate.
- Test the pressure: Measure the pressure at the pump discharge. This should meet the pressure requirements outlined in the system’s design criteria.
4. Measure System Performance
Ensure that the pump is delivering water at both the flow rate and pressure required for compliance. Typically, fire pumps should maintain a minimum pressure of 65 psi at the highest point of the system.
5. Verify Pump Performance Against Design Specifications
Compare the test results against the fire pump’s design specifications, which should be available in the system’s documentation. These include the flow rate (GPM) and pressure (PSI) requirements. If the results fall short, you’ll need to address the issue, whether by repairing or replacing components of the system.
6. Record and Report the Results
Document the results of the flow test, including:
- Date of test.
- Water flow rate (GPM).
- Pressure readings (PSI).
- Any discrepancies or issues encountered.
If the pump fails to meet the required flow or pressure specifications, the system may need repairs or modifications. Notify the relevant authorities or maintenance teams to take corrective actions.
7. Follow-Up Maintenance
Regular fire pump flow testing ensures your fire pump continues to meet safety standards and remain operational. If your system fails the test, routine maintenance and replacement of aging components can prevent future issues. Conduct annual flow tests and maintenance as required by NFPA 25.
Conclusion
Conducting a fire pump flow test for compliance is a critical step in maintaining a reliable fire protection system. By following the steps above, you ensure that your fire pump operates effectively in an emergency, and your facility remains compliant with national fire safety standards. Regular testing, along with proper maintenance, keeps the system in top condition and provides peace of mind that your fire safety measures are ready when needed most.