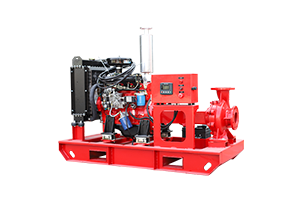
How does a flood control pump truck work?
Dec 19, 2023
Share:
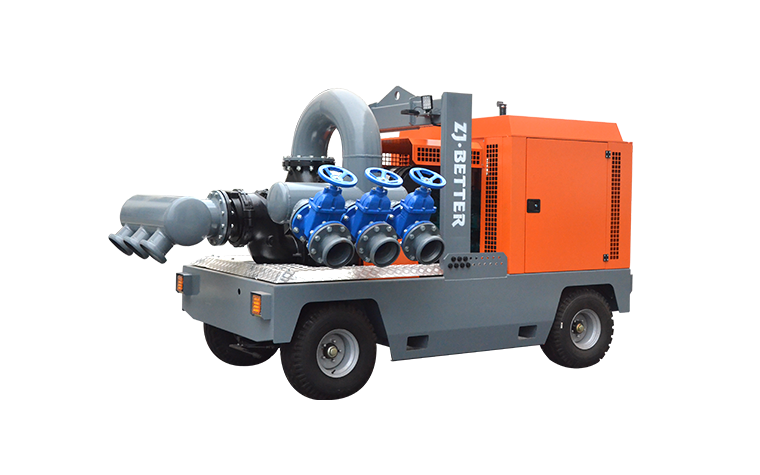
A flood control pump truck is designed to remove and transfer large volumes of water quickly, helping to control and mitigate flooding in various settings. Here's a general overview of how these pump trucks work:
1. **Pump Mechanism:**
- Flood control pump trucks are equipped with powerful pumps that can handle large quantities of water. These pumps are often centrifugal pumps, which use the rotation of an impeller to create a flow of water.
2. **Intake and Outlet:**
- The pump truck is positioned near the flooded area, and its intake hose or system is placed in the water source, such as a flooded street or area. The intake system draws water into the pump.
3. **Impeller Action:**
- As water is drawn into the pump, the impeller spins rapidly, creating a centrifugal force. This force pressurizes the water and propels it towards the outlet.
4. **Discharge:**
- The pressurized water is then discharged through an outlet hose or pipe. This discharge hose is directed away from the flooded area, often into a drainage system or another safe location.
5. **Mobility:**
- Flood control pump trucks are mounted on mobile platforms, such as trucks or trailers, allowing them to be quickly deployed to areas experiencing flooding. This mobility is crucial for rapid response to emergency situations.
6. **Power Source:**
- These pump trucks are typically powered by internal combustion engines, which provide the necessary power to drive the pump mechanism.
7. **Control Systems:**
- The operation of the pump, including the speed and flow rate, is controlled by the operator. Some pump trucks may have automated systems for more precise control.
8. **Versatility:**
- Flood control pump trucks are versatile and can be used in various settings, including urban and rural areas. They are commonly used in emergency response situations, construction sites, and flood-prone regions.
It's important to note that specific features and functionalities can vary among different models and manufacturers of flood control pump trucks. The overall goal is to efficiently remove water from flooded areas to prevent or minimize damage.

1. **Pump Mechanism:**
- Flood control pump trucks are equipped with powerful pumps that can handle large quantities of water. These pumps are often centrifugal pumps, which use the rotation of an impeller to create a flow of water.
2. **Intake and Outlet:**
- The pump truck is positioned near the flooded area, and its intake hose or system is placed in the water source, such as a flooded street or area. The intake system draws water into the pump.
3. **Impeller Action:**
- As water is drawn into the pump, the impeller spins rapidly, creating a centrifugal force. This force pressurizes the water and propels it towards the outlet.
4. **Discharge:**
- The pressurized water is then discharged through an outlet hose or pipe. This discharge hose is directed away from the flooded area, often into a drainage system or another safe location.
5. **Mobility:**
- Flood control pump trucks are mounted on mobile platforms, such as trucks or trailers, allowing them to be quickly deployed to areas experiencing flooding. This mobility is crucial for rapid response to emergency situations.
6. **Power Source:**
- These pump trucks are typically powered by internal combustion engines, which provide the necessary power to drive the pump mechanism.
7. **Control Systems:**
- The operation of the pump, including the speed and flow rate, is controlled by the operator. Some pump trucks may have automated systems for more precise control.
8. **Versatility:**
- Flood control pump trucks are versatile and can be used in various settings, including urban and rural areas. They are commonly used in emergency response situations, construction sites, and flood-prone regions.
It's important to note that specific features and functionalities can vary among different models and manufacturers of flood control pump trucks. The overall goal is to efficiently remove water from flooded areas to prevent or minimize damage.