Common Reasons for Fire Pump Failure to Start Normally
Jun 26, 2023
Share:
Introduction:
The proper functioning of fire pumps is critical for effective fire suppression and protection. However, there are instances when fire pumps fail to start normally, compromising their ability to respond promptly to fire emergencies. This essay explores the common reasons behind the failure of fire pumps to start normally, emphasizing the importance of identifying and addressing these issues to ensure reliable operation.
Electrical Issues:
Electrical problems are a frequent cause of fire pump startup failures. Issues such as loose connections, faulty wiring, or tripped circuit breakers can interrupt the power supply to the pump. Additionally, problems with the motor starter or control panel can prevent the pump from receiving the necessary electrical signals to initiate the startup sequence. Regular inspections, maintenance, and testing of electrical components are essential to identify and rectify any potential electrical issues that may hinder the normal startup of the fire pump.
Fuel Supply Problems (For Diesel-driven Pumps):
For diesel-driven fire pumps, insufficient or contaminated fuel can prevent normal startup. Inadequate fuel levels, clogged filters, or the presence of water or debris in the fuel can impede the proper functioning of the engine. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the fuel system, including fuel quality checks, filter replacements, and fuel tank cleanliness, are crucial to ensure uninterrupted fuel supply and prevent startup issues.
Mechanical Malfunctions:
Mechanical failures can also hinder the normal startup of fire pumps. Issues such as worn-out belts, damaged impellers, seized bearings, or malfunctioning pressure switches can prevent the pump from initiating or maintaining the required water flow and pressure. Routine inspections and preventive maintenance practices, including lubrication, belt replacements, and impeller inspections, are essential to identify and rectify any mechanical problems that may impede the startup process.
Control System or Sensor Failures:
Control system or sensor failures can cause fire pumps to malfunction during startup. Faulty pressure sensors, float switches, or control panel malfunctions can disrupt the pump's startup sequence or prevent it from reaching the desired operational parameters. Regular calibration and testing of control systems and sensors, along with prompt replacement of any faulty components, are crucial to ensure accurate readings and proper functioning during the startup process.
Lack of Maintenance and Testing:
The lack of regular maintenance and testing can lead to fire pump startup failures. Over time, components may degrade, connections may loosen, and system parameters may drift from optimal levels. Without periodic inspections, preventive maintenance, and performance testing, these issues may go unnoticed, resulting in startup problems when they are most needed. Implementing a comprehensive maintenance program and adhering to recommended testing schedules are essential to identify and rectify potential problems, ensuring the fire pump's reliable startup and operation.
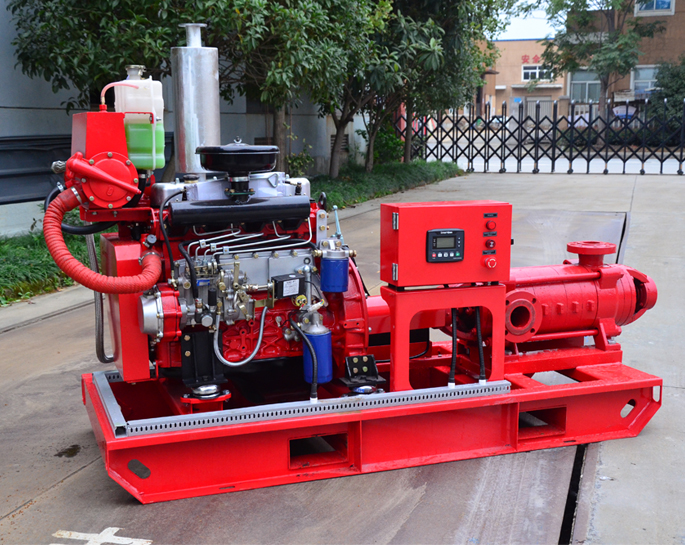

Conclusion:
Several factors can contribute to the failure of fire pumps to start normally. Electrical issues, fuel supply problems (for diesel-driven pumps), mechanical malfunctions, control system failures, and the lack of maintenance and testing are common culprits. Fire safety professionals must prioritize regular inspections, preventive maintenance, and performance testing to identify and address these issues promptly. By mitigating these potential causes of failure, fire pumps can start reliably and fulfill their critical role in protecting lives and property during fire emergencies.
The proper functioning of fire pumps is critical for effective fire suppression and protection. However, there are instances when fire pumps fail to start normally, compromising their ability to respond promptly to fire emergencies. This essay explores the common reasons behind the failure of fire pumps to start normally, emphasizing the importance of identifying and addressing these issues to ensure reliable operation.
Electrical Issues:
Electrical problems are a frequent cause of fire pump startup failures. Issues such as loose connections, faulty wiring, or tripped circuit breakers can interrupt the power supply to the pump. Additionally, problems with the motor starter or control panel can prevent the pump from receiving the necessary electrical signals to initiate the startup sequence. Regular inspections, maintenance, and testing of electrical components are essential to identify and rectify any potential electrical issues that may hinder the normal startup of the fire pump.
Fuel Supply Problems (For Diesel-driven Pumps):
For diesel-driven fire pumps, insufficient or contaminated fuel can prevent normal startup. Inadequate fuel levels, clogged filters, or the presence of water or debris in the fuel can impede the proper functioning of the engine. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the fuel system, including fuel quality checks, filter replacements, and fuel tank cleanliness, are crucial to ensure uninterrupted fuel supply and prevent startup issues.
Mechanical Malfunctions:
Mechanical failures can also hinder the normal startup of fire pumps. Issues such as worn-out belts, damaged impellers, seized bearings, or malfunctioning pressure switches can prevent the pump from initiating or maintaining the required water flow and pressure. Routine inspections and preventive maintenance practices, including lubrication, belt replacements, and impeller inspections, are essential to identify and rectify any mechanical problems that may impede the startup process.
Control System or Sensor Failures:
Control system or sensor failures can cause fire pumps to malfunction during startup. Faulty pressure sensors, float switches, or control panel malfunctions can disrupt the pump's startup sequence or prevent it from reaching the desired operational parameters. Regular calibration and testing of control systems and sensors, along with prompt replacement of any faulty components, are crucial to ensure accurate readings and proper functioning during the startup process.
Lack of Maintenance and Testing:
The lack of regular maintenance and testing can lead to fire pump startup failures. Over time, components may degrade, connections may loosen, and system parameters may drift from optimal levels. Without periodic inspections, preventive maintenance, and performance testing, these issues may go unnoticed, resulting in startup problems when they are most needed. Implementing a comprehensive maintenance program and adhering to recommended testing schedules are essential to identify and rectify potential problems, ensuring the fire pump's reliable startup and operation.

Conclusion:
Several factors can contribute to the failure of fire pumps to start normally. Electrical issues, fuel supply problems (for diesel-driven pumps), mechanical malfunctions, control system failures, and the lack of maintenance and testing are common culprits. Fire safety professionals must prioritize regular inspections, preventive maintenance, and performance testing to identify and address these issues promptly. By mitigating these potential causes of failure, fire pumps can start reliably and fulfill their critical role in protecting lives and property during fire emergencies.