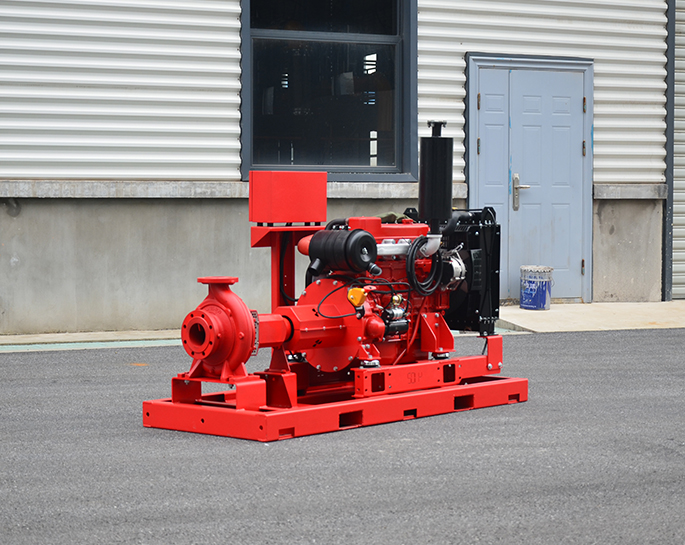
Are Diesel Engine Fire Pumps More Powerful?
Diesel engine fire pumps are often considered more robust in terms of power and reliability compared to electric fire pumps, especially in certain situations. However, whether they are "more powerful" depends on various factors like the specific needs of the fire protection system, the capacity of the pump, and the availability of power sources.
Here are some key factors that determine the power and suitability of diesel engine fire pumps:
1. Independence from Electrical Grid:
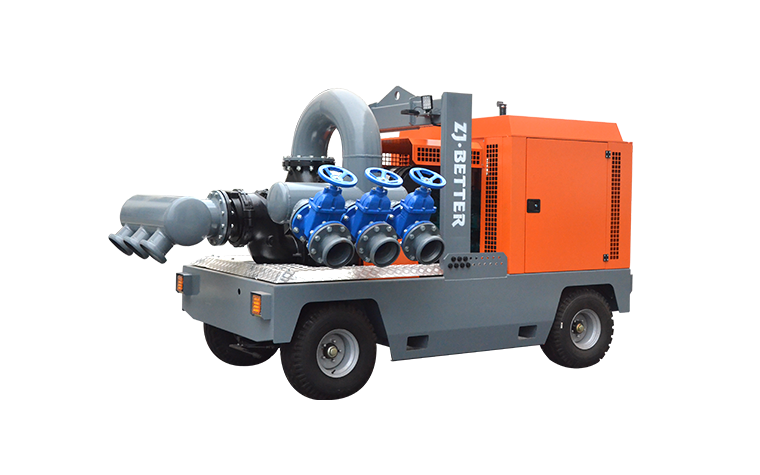
- Diesel Engine Fire Pumps: These pumps operate independently of the electrical grid, making them ideal for situations where electricity might be unreliable or during a power outage, such as in remote locations or during major fire incidents. This makes them powerful in the sense that they ensure continuous operation even when the power supply fails.
- Electric Fire Pumps: Rely on the electrical grid or backup generators, so if the power fails and there's no backup, they might not function.
2. Torque and Starting Power:
- Diesel Engine Pumps: Diesel engines generally have higher torque at lower RPMs compared to electric motors. This means they can handle higher loads more easily and are more capable of overcoming mechanical resistance, which could be beneficial when handling high-pressure fire suppression systems.
- Electric Fire Pumps: Electric motors, while quick to start, often don’t deliver the same level of torque or power as a diesel engine, especially in situations that require a heavy-duty performance. However, electric pumps are consistent and efficient for most standard applications.
3. Continuous Operation:
- Diesel Engine Fire Pumps: Designed for prolonged operation and can run for extended periods without overheating. This is critical for fighting large fires where uninterrupted water supply is needed for hours. Diesel pumps are often the preferred choice for high-risk, large-scale industrial applications.
- Electric Fire Pumps: Can run continuously but may require backup power systems to ensure operation if the fire lasts long or if the electrical supply fails.
4. Power Output and Flow Capacity:
- Diesel Engine Fire Pumps: Typically come in larger capacities, allowing them to provide higher water flow and pressure. They are often chosen for larger buildings or industrial sites that require more powerful fire protection systems.
- Electric Fire Pumps: Available in various sizes and capacities, they are commonly used in smaller or medium-sized buildings where the demand for high water flow is lower. For certain high-demand systems, however, they may require a more complex electrical infrastructure.
5. Application:
- Diesel Engine Fire Pumps: Often used in facilities where reliability and high performance are paramount, such as industrial plants, high-rise buildings, and remote sites. Diesel pumps are ideal when there's no assured power supply.
- Electric Fire Pumps: Commonly found in urban environments where electricity is stable. They're quieter, more environmentally friendly, and often preferred for small to medium-sized systems.
6. Maintenance:
- Diesel Engine Fire Pumps: Require more regular maintenance due to the complexities of the engine, including fuel supply, filters, and engine components.
- Electric Fire Pumps: Easier to maintain and tend to be more cost-effective for routine upkeep compared to diesel engines.
Conclusion:
Diesel engine fire pumps can be more powerful and reliable in terms of raw power, torque, and independence from electrical sources, making them ideal for large-scale, high-risk installations. However, electric pumps can also be powerful but are more suited to situations where consistent electrical power is guaranteed.
Would you like to explore options for diesel engine fire pumps for your specific needs at Better Pump?